Was tut sich in den Laboren von Universitäten oder F&E-Abteilungen der Unternehmen? In exklusiven Publikationen teilen Wissenschaftler aus aller Welt ihre aktuellen Erkenntnisse.
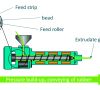
Optimization of Pressure and throughput Fluctuations of a cold-fed Rubber Extruder by means of a separately driven Feed Roller
In rubber extrusion, stable pressure and throughput over time is of central importance for the quality of the extrudate. One challenge is the non-uniform material intake of feed strips. Variable feed behaviour causes pressure and throughput fluctuations in the feed zone, which propagate to the die and may lead to dimensional deviations of the extrudate. The feed roller speed can influence the intake of the feed strip and therefore help to keep steady the pressure in the feed zone. Thanks to a measurement of the drive torques from the screw and the feed roller, deviations in the feeding can quickly be identified.Weiterlesen...

Modelling Study of Reinforcement and Rupture in Strain Crystallizing Elastomer Networks
The model for strain-induced crystallization (SIC) in elastomer networks proposed by Plagge and Hentschke [1] is extended for the simulation of rupture. A critical force for rupture of links, i.e. the polymer chains in the model network, is defined. The variation of parameters which affect the structure of the networks or the free energy of the links has not improved the tensile strength of strain-crystallizing networks compared to non-crystallizing networks in both the 2D- and the 3D-case. Thus, a critical crystallinity is introduced. If the crystallinity of a link exceeds this threshold, the link becomes unbreakable. The tensile strength of crystallizing 2D- and 3D-networks has improved significantly.Weiterlesen...
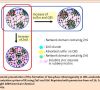
Sophisticated Vulcanization of Rubber
This paper presents of sophisticated aspects of the N-(1,3-benzothiazol-2-ylsulfanyl)cyclohexanamine-accelerated vulcanization of isoprene rubber (IR) as a mini-reviewed, where zinc oxide (ZnO), stearic acid (StH) and/or zinc stearate are used as activators. The combination of these activators enables the control of the mesh size in the network, where new complexes are generated by a reaction of ZnO with StH, or by zinc stearate near the vulcanization temperature. The complexes accelerate the sulfur cross-linking of IR like an enzyme. An electron-transfer and a dispersion effects of IR for the complexes play roles of the acceleration of cross-linking and the formation of homogeneous network structure, respectively. In addition, the complexes predominantly generate the disulfidic linkages in the sulfur cross-linking.Weiterlesen...
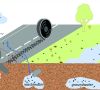
Tire Wear Particles
Tire wear significantly contributes to the growing amount of microplastic in the environment. It is found in the waters and in the soils, meanwhile also in living beings.Weiterlesen...
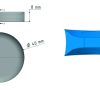
Numerical Studies on the Dissipation behavior of Elastomers and its Effect on the applied loading Conditions
The aim of this paper is to discuss the effect of the viscoelasticity and dissipation behavior of elastomers on the applied loading conditions. For that purpose, the loading applied on the rotary dynamic testing machine designed by Gent [1] is simulated. The material model used in the simulation is a finite viscoelastic model based on the multiplicative decomposition of the deformation gradient.Weiterlesen...
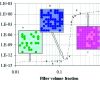
Similarities in Stress-Strain-Curve and electrical Conductivity
Electroconductive composites were prepared using either styrene–butadiene rubber or polycaprolactone matrix with varying amounts of two grades of electroconductive carbon black. Electrical conductivity was measured during deformation and at the same time a stress-strain-curve was recorded. The dependences of electrical conductivity on deformation exhibit several extremes. All conductivity changes were interpreted in terms of either the conductive pathways destruction or the formation of new ones, Thus, electrical conductivity can be correlated with the specific features of the physical network of the reinforcing filler that affect the mechanical properties of the composite.Weiterlesen...
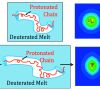
Molecular-Scale Polymer Melts Response to shear in the linear and non-linear rheological
The molecular-level response to shear of entangled polymers at interfaces and in the bulk has been of interest to understand the non-linear rheological response of polymers. Here we focus on the molecular level response to shear strain leading non-linear rheological phenomenon, in linear and star polymers comparing the observed response to the predictions of tube theory. We used SANS measurements of the bulk polymer response to shear in Couette geometry on melts of high molecular weight mixtures of polymers extending our previous results on interfacial responses with rheoNR measurements in cone-and-plate geometry.[1, 2] further development of the theory.Weiterlesen...

Influence of Process Parameters on the Curing of Polyurethanes by dielectric Measurements
The Polyurethane Reaction Injection Molding (PU RIM) process is currently still reliant on a high level of know-how, both in the case of quality deviations of the product and in the initial configuration of molds. PU manufacturing hardly uses the established sensor technologies that are common in injection molding. In a research project at the Institute for Plastics Processing (IKV), the influence of the process parameters component temperature, mold temperature, material output speed and mixing ratio on the curing behavior of compact polyurethane coating systems is being experimentally investigated by means of dielectric measurements. The results show that for all variations of the process parameters investigated, the influence on the curing reaction could be successfully detected.Weiterlesen...
Evaluation of the Reinforcement Mechanism of functionalized Nanoparticles in Silica loaded Rubber Compounds
The performance of nano-sized rubber particles with different functional groups was studied in a silica loaded tire tread compound. The nanoparticles contained hydroxyl-, carboxyl-, dimethyl amino-, pyridino-, or epoxy- groups. In uncured compounds the reduction of filler flocculation at 160°C was mostly pronounced by nanoparticles, which contained either carboxyl or hydroxyl groups. In vulcanizates, the best filler dispersion and the best combination of mechanical and dyn.- mechanical properties were obtained with nanoparticles with OH-groups. As the silanization of the OH-groups is much slower than that of the silanol groups the OH-groups of the nanoparticles are practically not silanized at the end of the compounding procedure.Weiterlesen...
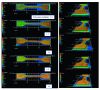
Additive Manufacturing of Rubber Parts based on low viscous Compounds using a Direct-Ink-Writing Process
This paper deals with investigations into the additive manufacturing of an EPDM-based high-viscosity sulfur-curable rubber compound. In order to make the compound processible using „Direct-Ink-Writing“, different solvent concentrations are used to reduce the compound viscosity to the limited process window. For 3D-printing process variable process parameters are used to optimize the quality of the rubber part, which is controlled by laser confocal microscope, 3D-µ-CT and physical properties. In addition, the effect of residual solvent in the polymer, respectively in the semi-finished product, affect the possible volume shrinkage caused by evaporation processes of the printed part during vulcanization.Weiterlesen...