 ELASTOMERS AND PLASTICS
An Examination of the Degree of Crosslink Distribution Heterogeneity in Nitrile Rubber by Double Quantum Nuclear magnetic Resonance
ELASTOMERS AND PLASTICS
An Examination of the Degree of Crosslink Distribution Heterogeneity in Nitrile Rubber by Double Quantum Nuclear magnetic Resonance
The properties of carbon black reinforced sulfur or peroxide cured nitrile rubber (18 to 49% ACN) compounds were measured by rheology, hardness, stress-strain characteristics and Double Quantum (DQ) Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) while the elastomer monomer sequencing levels were assessed by liquid 1 H NMR.
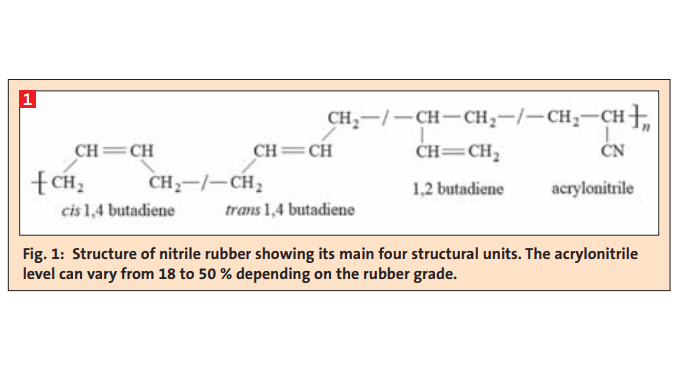
Nitrile rubber is manufactured through the use of a radical based emulsion polymerization be-tween acrylonitrile (ACN) and butadiene (BD) resulting in a statistical copolymer structure (see Fig. 1). The ACN level of its chemical composition is the primary factor in differentiating nitrile grades with respect to oil, grease and fuel resistance. An increase in ACN concentration brings about an enhancement in hardness, tensile strength and modulus with an accompanying reduction in compression set, low temperature flexibility and gas permeability in the vulcanizate. Besides the dominant role of ACN concentration, the NBR microstructure (i.e., unsaturation level, ratio of 1,2 to 1,4 butadiene structures, degree of branching/crosslinking, monomer sequencing, molecular weight and its distribution) has a certain influence of the final compound state on cure and ensuing vulcanizate properties.
-
473,00 € / Jahr
-
Jederzeit kündbar
Sie haben bereits ein Konto? Hier einloggen



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ac/4c/ac4c91e3f302ceb89613ed910c2b0929/adobestock-292127146-4053x2283v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/39/5839e44836a58e3cf7d352d3210dc7d8/wdk-pressefoto-20michael-20klein-1920x1080v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/6e/47/6e473ad518365a09db0d389387c5b82a/csm-banner-005-problemloesungen-01-2a8d75b173-1068x600v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/85/3b853d5a7c8fa5640146edb920e59526/pxl-20250616-161225541-mp-4032x2266v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/1e/04/1e04e410d83b193519e83cbc2a7566ff/silpuran-medical-adhesives-2303x1295v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/42/0b/420bf691d7454a85327a80ad53c45b94/thumbnail-rado-online-strainer-1772x996v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/b9/cd/b9cd9b5b904a2b3df8c5aaa7b98edc2c/kraiburg-20gummiwerk-20vmq-5712x3210v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/80/bc/80bcfb071d0b136eeb3e00a006832fbb/2026--2002--2013--20fraunhofer-20imws-20aufmacher-3024x1701v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/85/59/855967f12a6f8ff1ed20371651cb1796/screenshot-202025-12-08-20130418-690x388v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ba/da/bada2c6c71c5232551c26cb5c7cc62e1/screenshot-202025-12-08-20131102-710x399v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/32/08/3208424a642b590ef57370b2ebb4e665/screenshot-202025-12-08-20123833-946x532v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/13/4c/134c673ee6edc454febfc844a7ede791/bildunterschrift-201-uth-trp-blending-3024x1702v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/07/56/075632bff9a9d7c9b5a44c50775c7d8b/aufmacher-g-c3-b6tz-scheibe-6000x3373v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/09/60095a181e6b56953727a6b89c362055/extruder-5472x3076v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/d8/58d87b00fb0bcda2cc265da60eab6270/4-zentr--l-c3-bcftg-ger-c3-a4t-mit-w-c3-a4rmer-c3-bcck-und-kws-3507x1973v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/02/30/02306299c3bdf32e7b856bc4e0d205bf/tempro-20basic-20120-6635x3732v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4b/5b/4b5bc2686b3643dd079a03b312ee0608/reifen-labor-abrieb-1536x864v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/9d/3b9d2095a8ebe7a56d7af8b1bc838d65/vdwf-azubi-up-01-5a70602339-1200x675v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/9d/609d1bf747c52a8a56a2f6ddf2144b43/deguma-walzwerk-aufmacher-367x206v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/23/34/23343ab8023801ac334b2f06fdeae24f/remberg-visual-copryright-remberg-5304x2983v1.png)