 TESTING AND MEASURING
Comparative Advantages of different RPA-ASTM Methods for Detecting Rubber Compound Quality Differences
TESTING AND MEASURING
Comparative Advantages of different RPA-ASTM Methods for Detecting Rubber Compound Quality Differences
Over the last three decades, the Rubber Process Analyzer has evolved as the processability test instrument of choice for measuring and solving many rubber factory problems. Also, a new ASTM reflective microscope method is also commonly used.
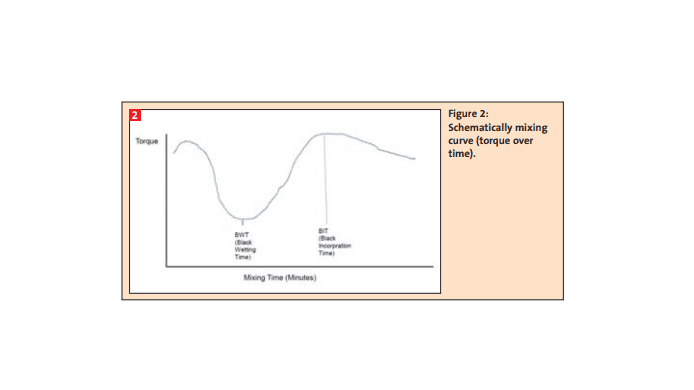
During the mixing process for a rubber compound, the base elastomer is masticated while the other ingredients, such as carbon black, begin to incorporate. As this process continues, the carbon black agglomerates are deagglomerated and dispersed as primary aggregates while the base raw elastomer(s) is simultaneously masticated and ”broken down” usually through some degree of depolymerization [1,2]. We constructed simple model recipes of selected fillers with SBR and studied the rheological effects on these experimental compounds from controlled amounts of applied work history during BR Banbury mixing in the laboratory.
-
473,00 € / Jahr
-
Jederzeit kündbar
Sie haben bereits ein Konto? Hier einloggen



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ac/4c/ac4c91e3f302ceb89613ed910c2b0929/adobestock-292127146-4053x2283v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/39/5839e44836a58e3cf7d352d3210dc7d8/wdk-pressefoto-20michael-20klein-1920x1080v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/6e/47/6e473ad518365a09db0d389387c5b82a/csm-banner-005-problemloesungen-01-2a8d75b173-1068x600v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/85/3b853d5a7c8fa5640146edb920e59526/pxl-20250616-161225541-mp-4032x2266v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/1e/04/1e04e410d83b193519e83cbc2a7566ff/silpuran-medical-adhesives-2303x1295v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/42/0b/420bf691d7454a85327a80ad53c45b94/thumbnail-rado-online-strainer-1772x996v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/b9/cd/b9cd9b5b904a2b3df8c5aaa7b98edc2c/kraiburg-20gummiwerk-20vmq-5712x3210v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/80/bc/80bcfb071d0b136eeb3e00a006832fbb/2026--2002--2013--20fraunhofer-20imws-20aufmacher-3024x1701v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/85/59/855967f12a6f8ff1ed20371651cb1796/screenshot-202025-12-08-20130418-690x388v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ba/da/bada2c6c71c5232551c26cb5c7cc62e1/screenshot-202025-12-08-20131102-710x399v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/32/08/3208424a642b590ef57370b2ebb4e665/screenshot-202025-12-08-20123833-946x532v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/13/4c/134c673ee6edc454febfc844a7ede791/bildunterschrift-201-uth-trp-blending-3024x1702v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/07/56/075632bff9a9d7c9b5a44c50775c7d8b/aufmacher-g-c3-b6tz-scheibe-6000x3373v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/09/60095a181e6b56953727a6b89c362055/extruder-5472x3076v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/d8/58d87b00fb0bcda2cc265da60eab6270/4-zentr--l-c3-bcftg-ger-c3-a4t-mit-w-c3-a4rmer-c3-bcck-und-kws-3507x1973v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/02/30/02306299c3bdf32e7b856bc4e0d205bf/tempro-20basic-20120-6635x3732v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4b/5b/4b5bc2686b3643dd079a03b312ee0608/reifen-labor-abrieb-1536x864v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/9d/3b9d2095a8ebe7a56d7af8b1bc838d65/vdwf-azubi-up-01-5a70602339-1200x675v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/9d/609d1bf747c52a8a56a2f6ddf2144b43/deguma-walzwerk-aufmacher-367x206v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/23/34/23343ab8023801ac334b2f06fdeae24f/remberg-visual-copryright-remberg-5304x2983v1.png)