 TESTING AND MEASURING
Measurement of Wall Shear Stress for Identification of Wall Slip Effects in Rubber Compounds
TESTING AND MEASURING
Measurement of Wall Shear Stress for Identification of Wall Slip Effects in Rubber Compounds
The wall slip of various rubber compounds has far-reaching effects on the design of extrusion dies and extruder screws as well as on viscosity measurements. However, in most cases it is not possible to determine under which circumstances a compound adheres to the wall or slides.
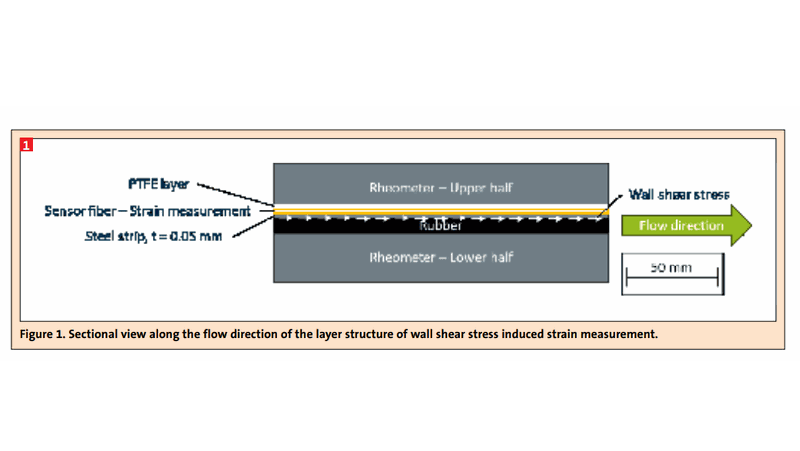
Rheological material data and empirically determined material laws are used in order to design extrusion and injection moulding dies and screws. However, wall-slipping fluids pose a challenge when determining this material data. For example during viscosity measurements in a high pressure capillary rheometer, wall slip does not typically occur over the entire capillary length but only sets in at lower pressures. The exact point depends on the material itself.
-
473,00 € / Jahr
-
Jederzeit kündbar
Sie haben bereits ein Konto? Hier einloggen



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/85/3b853d5a7c8fa5640146edb920e59526/pxl-20250616-161225541-mp-4032x2266v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/a4/74/a4744b9ccd6b408173c422b918b8b11f/ulrich-reifenh-c3-a4user-3000x1688v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/72/66/72667830daf063f3e7d859498a6b0cbd/bild-2001-20gesch-c3-a4ftsf-c3-bchrung-20-c2-a9-20nexus-4032x2268v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/98/69/9869205e6343e4f9ee68360d25a0398e/aufmacher-799x449v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/42/0b/420bf691d7454a85327a80ad53c45b94/thumbnail-rado-online-strainer-1772x996v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/b9/cd/b9cd9b5b904a2b3df8c5aaa7b98edc2c/kraiburg-20gummiwerk-20vmq-5712x3210v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/8d/22/8d224a120bec1c131fb630ba91178708/kraiburg-tpe-fr-1934x1087v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/85/59/855967f12a6f8ff1ed20371651cb1796/screenshot-202025-12-08-20130418-690x388v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ba/da/bada2c6c71c5232551c26cb5c7cc62e1/screenshot-202025-12-08-20131102-710x399v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/32/08/3208424a642b590ef57370b2ebb4e665/screenshot-202025-12-08-20123833-946x532v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/9f/ce/9fce39cae6873087a7a488e41b2c99ef/screenshot-202025-12-08-20125029-700x394v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/13/4c/134c673ee6edc454febfc844a7ede791/bildunterschrift-201-uth-trp-blending-3024x1702v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/07/56/075632bff9a9d7c9b5a44c50775c7d8b/aufmacher-g-c3-b6tz-scheibe-6000x3373v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/09/60095a181e6b56953727a6b89c362055/extruder-5472x3076v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/d8/58d87b00fb0bcda2cc265da60eab6270/4-zentr--l-c3-bcftg-ger-c3-a4t-mit-w-c3-a4rmer-c3-bcck-und-kws-3507x1973v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/02/30/02306299c3bdf32e7b856bc4e0d205bf/tempro-20basic-20120-6635x3732v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4b/5b/4b5bc2686b3643dd079a03b312ee0608/reifen-labor-abrieb-1536x864v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/9d/3b9d2095a8ebe7a56d7af8b1bc838d65/vdwf-azubi-up-01-5a70602339-1200x675v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/9d/609d1bf747c52a8a56a2f6ddf2144b43/deguma-walzwerk-aufmacher-367x206v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/23/34/23343ab8023801ac334b2f06fdeae24f/remberg-visual-copryright-remberg-5304x2983v1.png)