 CONSTRUCTION AND SIMULATION
Optimisation of the Simulation of Rubber Extrusion dies by means of the Integration of empirically determined characteristic Maps
CONSTRUCTION AND SIMULATION
Optimisation of the Simulation of Rubber Extrusion dies by means of the Integration of empirically determined characteristic Maps
Anbieter zum Thema
By determining characteristic maps that describe the wall slip as a function of the compound composition and the extrusion temperature, boundary conditions in flow simulations can be determined in such a way that the effects on pressure and temperature distribution in the extrusion process are considered.
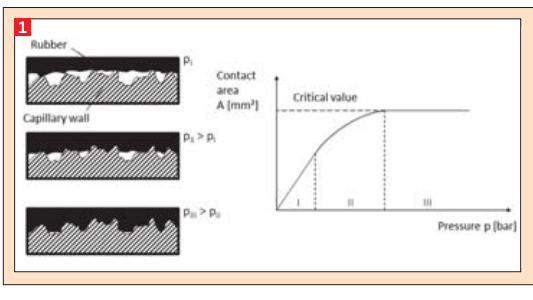
hen designing extrusion dies for rubbers, the complex flow behaviour, which is characterised by the presence of rather high wall shear stresses leading to significant viscous dissipation and - in combination with the presence of plasticisers - a tendency towards wall slip, poses a particular challenge. This means that effects such as viscous dissipation, wall slip and swelling affect the design of the die, as these have a significant influence on the surface quality and dimensional accuracy of the extrudates. To understand these phenomena in depth, first the basics of the rubber rheology have to be discussed.
-
473,00 € / Jahr
-
Jederzeit kündbar
Sie haben bereits ein Konto? Hier einloggen



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ac/4c/ac4c91e3f302ceb89613ed910c2b0929/adobestock-292127146-4053x2283v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/39/5839e44836a58e3cf7d352d3210dc7d8/wdk-pressefoto-20michael-20klein-1920x1080v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/6e/47/6e473ad518365a09db0d389387c5b82a/csm-banner-005-problemloesungen-01-2a8d75b173-1068x600v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/85/3b853d5a7c8fa5640146edb920e59526/pxl-20250616-161225541-mp-4032x2266v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/1e/04/1e04e410d83b193519e83cbc2a7566ff/silpuran-medical-adhesives-2303x1295v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/42/0b/420bf691d7454a85327a80ad53c45b94/thumbnail-rado-online-strainer-1772x996v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/b9/cd/b9cd9b5b904a2b3df8c5aaa7b98edc2c/kraiburg-20gummiwerk-20vmq-5712x3210v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/80/bc/80bcfb071d0b136eeb3e00a006832fbb/2026--2002--2013--20fraunhofer-20imws-20aufmacher-3024x1701v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/85/59/855967f12a6f8ff1ed20371651cb1796/screenshot-202025-12-08-20130418-690x388v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ba/da/bada2c6c71c5232551c26cb5c7cc62e1/screenshot-202025-12-08-20131102-710x399v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/32/08/3208424a642b590ef57370b2ebb4e665/screenshot-202025-12-08-20123833-946x532v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/13/4c/134c673ee6edc454febfc844a7ede791/bildunterschrift-201-uth-trp-blending-3024x1702v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/07/56/075632bff9a9d7c9b5a44c50775c7d8b/aufmacher-g-c3-b6tz-scheibe-6000x3373v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/09/60095a181e6b56953727a6b89c362055/extruder-5472x3076v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/d8/58d87b00fb0bcda2cc265da60eab6270/4-zentr--l-c3-bcftg-ger-c3-a4t-mit-w-c3-a4rmer-c3-bcck-und-kws-3507x1973v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/02/30/02306299c3bdf32e7b856bc4e0d205bf/tempro-20basic-20120-6635x3732v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4b/5b/4b5bc2686b3643dd079a03b312ee0608/reifen-labor-abrieb-1536x864v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/9d/3b9d2095a8ebe7a56d7af8b1bc838d65/vdwf-azubi-up-01-5a70602339-1200x675v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/9d/609d1bf747c52a8a56a2f6ddf2144b43/deguma-walzwerk-aufmacher-367x206v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/23/34/23343ab8023801ac334b2f06fdeae24f/remberg-visual-copryright-remberg-5304x2983v1.png)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/68/76/68762a9100b6f/kreiburg.png)