 RAW MATERIALS AND APPLICATIONS
The Effect of different Silanes to Lignin Dispersion and Rubber-Filler Interaction in
RAW MATERIALS AND APPLICATIONS
The Effect of different Silanes to Lignin Dispersion and Rubber-Filler Interaction in
Lignin holds a promise to act as a sustainable reinforcing filler in rubber industry, replacing carbon black and silica. However, poor dispersion and weak rubber-filler interaction have hindered the use of lignin.
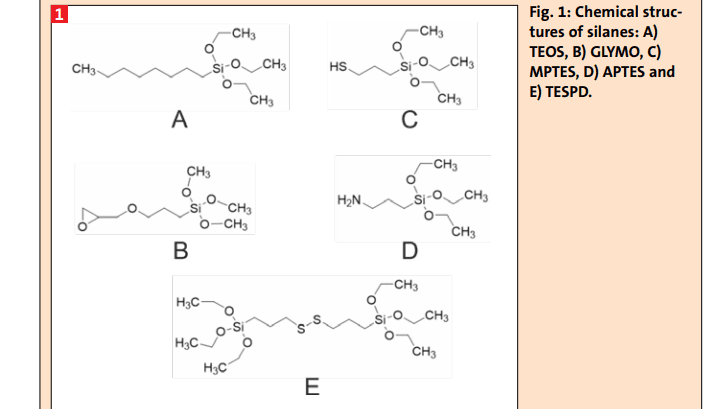
Fillers are used in elastomers for various purposes, primarily to enhance the mechanical properties and reduce material costs. The most commonly used reinforcing fillers are carbon black and silica. To fully exploit the reinforcing potential of fillers, it is essential to achieve homogenous dispersion and distribution of the filler, as well as strong interaction between the filler and the polymer matrix. There are several methods to enhance the rubber-filler interaction, including the addition of functional groups to the polymer, the use of coupling agents and surface modification of fillers.
-
473,00 € / Jahr
-
Jederzeit kündbar
Sie haben bereits ein Konto? Hier einloggen



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ac/4c/ac4c91e3f302ceb89613ed910c2b0929/adobestock-292127146-4053x2283v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/39/5839e44836a58e3cf7d352d3210dc7d8/wdk-pressefoto-20michael-20klein-1920x1080v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/6e/47/6e473ad518365a09db0d389387c5b82a/csm-banner-005-problemloesungen-01-2a8d75b173-1068x600v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/85/3b853d5a7c8fa5640146edb920e59526/pxl-20250616-161225541-mp-4032x2266v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/1e/04/1e04e410d83b193519e83cbc2a7566ff/silpuran-medical-adhesives-2303x1295v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/42/0b/420bf691d7454a85327a80ad53c45b94/thumbnail-rado-online-strainer-1772x996v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/b9/cd/b9cd9b5b904a2b3df8c5aaa7b98edc2c/kraiburg-20gummiwerk-20vmq-5712x3210v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/80/bc/80bcfb071d0b136eeb3e00a006832fbb/2026--2002--2013--20fraunhofer-20imws-20aufmacher-3024x1701v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/85/59/855967f12a6f8ff1ed20371651cb1796/screenshot-202025-12-08-20130418-690x388v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ba/da/bada2c6c71c5232551c26cb5c7cc62e1/screenshot-202025-12-08-20131102-710x399v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/32/08/3208424a642b590ef57370b2ebb4e665/screenshot-202025-12-08-20123833-946x532v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/13/4c/134c673ee6edc454febfc844a7ede791/bildunterschrift-201-uth-trp-blending-3024x1702v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/07/56/075632bff9a9d7c9b5a44c50775c7d8b/aufmacher-g-c3-b6tz-scheibe-6000x3373v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/09/60095a181e6b56953727a6b89c362055/extruder-5472x3076v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/d8/58d87b00fb0bcda2cc265da60eab6270/4-zentr--l-c3-bcftg-ger-c3-a4t-mit-w-c3-a4rmer-c3-bcck-und-kws-3507x1973v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/02/30/02306299c3bdf32e7b856bc4e0d205bf/tempro-20basic-20120-6635x3732v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4b/5b/4b5bc2686b3643dd079a03b312ee0608/reifen-labor-abrieb-1536x864v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/9d/3b9d2095a8ebe7a56d7af8b1bc838d65/vdwf-azubi-up-01-5a70602339-1200x675v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/9d/609d1bf747c52a8a56a2f6ddf2144b43/deguma-walzwerk-aufmacher-367x206v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/23/34/23343ab8023801ac334b2f06fdeae24f/remberg-visual-copryright-remberg-5304x2983v1.png)