 TESTING AND MEASURING
Wall Slip in Processing Rubber Compound revisited
TESTING AND MEASURING
Wall Slip in Processing Rubber Compound revisited
In a previous paper, we have presented an alternative way to use the RPA (Rubber Process Analyzer) to measure both transient and steady shear viscosity [1]. The replacement of the grooved upper die by a “mirror” polished groove less die combined with programmable internal pressure offers a unique combination to study wall slip. It unambiguously showed that the wall slip ratio is decreasing while increasing shear stress/rate. It demonstrates as well that wall slip depends upon pressure.
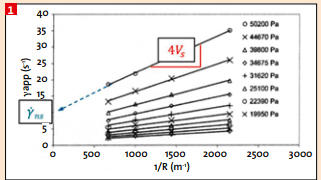
Industrial rubber compound processing is essentially performed by extrusion or injection molding. These processes are nowadays predicted using various flow modeling techniques. Prediction includes for extrusion, extruder output, die pressure and die swelling. In order to successfully achieve this goal, a correct flow model needs to be selected. This model then needs to be fed with meaningful rheological data. These data include shear viscosity and its depυυυendence to shear rate and temperature. This kind of measurement is commonly performed using a capillary rheometer.
-
473,00 € / Jahr
-
Jederzeit kündbar
Sie haben bereits ein Konto? Hier einloggen



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/85/3b853d5a7c8fa5640146edb920e59526/pxl-20250616-161225541-mp-4032x2266v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/a4/74/a4744b9ccd6b408173c422b918b8b11f/ulrich-reifenh-c3-a4user-3000x1688v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/72/66/72667830daf063f3e7d859498a6b0cbd/bild-2001-20gesch-c3-a4ftsf-c3-bchrung-20-c2-a9-20nexus-4032x2268v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/98/69/9869205e6343e4f9ee68360d25a0398e/aufmacher-799x449v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/42/0b/420bf691d7454a85327a80ad53c45b94/thumbnail-rado-online-strainer-1772x996v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/b9/cd/b9cd9b5b904a2b3df8c5aaa7b98edc2c/kraiburg-20gummiwerk-20vmq-5712x3210v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/8d/22/8d224a120bec1c131fb630ba91178708/kraiburg-tpe-fr-1934x1087v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/85/59/855967f12a6f8ff1ed20371651cb1796/screenshot-202025-12-08-20130418-690x388v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ba/da/bada2c6c71c5232551c26cb5c7cc62e1/screenshot-202025-12-08-20131102-710x399v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/32/08/3208424a642b590ef57370b2ebb4e665/screenshot-202025-12-08-20123833-946x532v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/9f/ce/9fce39cae6873087a7a488e41b2c99ef/screenshot-202025-12-08-20125029-700x394v1.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/13/4c/134c673ee6edc454febfc844a7ede791/bildunterschrift-201-uth-trp-blending-3024x1702v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/07/56/075632bff9a9d7c9b5a44c50775c7d8b/aufmacher-g-c3-b6tz-scheibe-6000x3373v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/09/60095a181e6b56953727a6b89c362055/extruder-5472x3076v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/58/d8/58d87b00fb0bcda2cc265da60eab6270/4-zentr--l-c3-bcftg-ger-c3-a4t-mit-w-c3-a4rmer-c3-bcck-und-kws-3507x1973v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/02/30/02306299c3bdf32e7b856bc4e0d205bf/tempro-20basic-20120-6635x3732v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4b/5b/4b5bc2686b3643dd079a03b312ee0608/reifen-labor-abrieb-1536x864v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/9d/3b9d2095a8ebe7a56d7af8b1bc838d65/vdwf-azubi-up-01-5a70602339-1200x675v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/9d/609d1bf747c52a8a56a2f6ddf2144b43/deguma-walzwerk-aufmacher-367x206v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/23/34/23343ab8023801ac334b2f06fdeae24f/remberg-visual-copryright-remberg-5304x2983v1.png)