Was tut sich in den Laboren von Universitäten oder F&E-Abteilungen der Unternehmen? In exklusiven Publikationen teilen Wissenschaftler aus aller Welt ihre aktuellen Erkenntnisse.
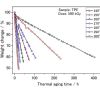
Effect of Gamma Ray Pre-Irradiation on Thermogravimetric
The changes of the thermal stability by gamma ray pre-irradiation on tetrafluoroethylene-propylene elastomer was studied by the measurement of the weight change. The weight decrease curves by thermal aging at constant temperatures were straight line. The activation energy calculated from the slope was 130 kJ/mol. The activation energy was obtained by also the thermogravimetric analysis. The value was from 143 kJ/mol to 157 kJ/mol with reference to ISO 11358-2. Friedman plot (ISO 11358-3) of the same TG curves showed the activation energy from 142 kJ/mol to 153 kJ/mol.Weiterlesen...

Investigation of the Foam Density Development of EPDM Rubber Foam using Thermoplastic Expandable Microspheres
The aim of these experimental investigations is to understand the potential for reducing foam density by the amount of Thermoplastic Expandable Microspheres (TEM) used as foaming agent, the processing temperature and the viscosity of the rubber. Two EPDM-based rubber compounds that are processed in injection moulding and ex-trusion processes, and therefore have different viscosities, have been the subject of investigation. A Sponge Rubber Analyzer is used to determine the time-dependent reduction and thus the lowest achievable foam density. It was shown that the process temperature and the mass content of TEM added had a significant influence on the foam density reduction.Weiterlesen...

Structural and Physical Properties of Poly Methyl Methacrylate / Magnetite Nanocomposites
The casting technique was used for the preparation of poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) nanoparticles at different concentrations of Fe3O4. SEM indicated a precise distribution of Fe3O4 particles in the PMMA matrix up to 10 wt%. XRD reveals an increase in crystallization by increasing the Fe3O4 content. The dielectric parameters ε‘ and ε“ were found to increase gradually by increasing Fe3O4 content up to 10 wt% followed by an abrupt increase. The electrical conductivity σdc at 30 °C was found to be in the order of 10-9 S cm-1 which recommends such composites to be used as antistatic materials. On the other hand, the values of σdc at 90 °C was found to be in the order of 10-3 S cm-1 which behave like semiconductor at such high temperature.Weiterlesen...
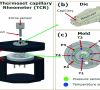
New Thermoset Capillary Rheometer (TCR) to evaluate Flow and Thermal Behavior of Thermosets
To evaluate flow and thermal properties of thermosetting materials at pressures comparable to processing operations, a new Thermoset Capillary Rheometer (TCR) is introduced. Material viscosity is measured before curing and during curing. This is used to determine the curing curve and gel time. Depending on the mold temperature, some compounds show decrease in pressure due to shrinkage whereas some other materials show increase in pressure due to degradation. As the pressure increases, shrinkage and degradation decrease. Thermal behavior of the compound during curing is monitored with gradient temperature sensors. The time at which the maximum exothermic peak happens correlates with curing speed.Weiterlesen...

Technikum für Hochviskosetechnologie von Covestro eröffnet
Das im Chempark in Leverkusen eingeweihte Technikum soll dazu beitragen, etablierte Kunststoffprodukte zu verbessern, neue Verfahren zu entwickeln und Produktionsprozesse zu optimieren. Im Forschungsfokus stehen beispielsweise Polycarbonatschmelzen.Weiterlesen...

Reduction of Triboelectrification of Polymeric Textiles
The present work investigates the effect of blending polyester (PET) and polyamide (PA) by carbon fibers (CF) in the form of simple weaves and sliding on cotton textile. It was revealed that electrostatic charge (ESC) decreased with increasing CF content. besides, after sliding ESC displayed higher values than that observed after contact-separation.Weiterlesen...

Application of recovered Carbon Black (rCB) from End-of-Life (EoL) tire Pyrolysis in Butyl Rubber Compounds
In the present study „Application of recovered Carbon Black (rCB) from End-of-Life Tire pyrolysis in butyl rubber compounds“, the research on the use of rCB in new butyl compounds is presented. In general, pyrolysis of scrap tires is considered a future-oriented additional technology regarding the lack of recycling capacities. While the pyrolysis products oil and gas already find industrial application, there is still a lack of suitable applications for the solid pyrolysis residue rCB. With its reuse in butyl blends, the study investigates a potential rCB sink.Weiterlesen...

Enhancing the Strength and Wear Resistance of Rocca Oil based Epoxy/TiO2 NPs Matrix as Eco-Friendly Reinforcements
This study investigates the mechanical, physical, and wear-resistant properties of different epoxy composites. An epoxy matrix is used as the base material, while a combination of rocca natural oil and TiO2 nanoparticles is used as filler. The experiments include XRD analysis, hardness measurements, stress-strain curve analysis, friction coefficient and wear rate calculations and topography examination of worn surfaces using optical 3D and SEM imaging. The results show that the hybrid filler is well-dispersed throughout the matrix according to XRD analysis. Additionally, filling the matrix with 1.5 % TiO2 nanoparticles and 10 % rocca/epoxy matrices increases the hardness value by approximately 13.3 %. The lowest friction coefficient and wear rate were found in the sample filled with 10 % rocca oil and 1 % TiO2 nanoparticles, with reductions of 61 % and 70 %, respectively.Weiterlesen...
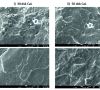
Perspective Application of Biopolymers as Components of Rubber Compounds
Biodegradable and environmentally friendly polymers made from renewable raw materials are now the preferred choice for a wide range of applications. However, a combination of petroleum and bio-based sources is now being studied for developing cost-effective and environmentally friendly rubber products, with a specific pursuit of the European Green Deal. This research is focused on the application of calcium lignosulfonate into NBR rubber. The incorporation of plasticizer into the rubber compounds aimed to plasticize the biopolymer, to achieve a higher degree of homogeneity, improve the interfacial adhesion between the biopolymer and rubber matrix, and consequently achieve improved mechanical properties. The obtained results clearly show that it is possible to incorporate calcium lignosulfonate into the rubber matrix and to achieve the required characteristics of prepared vulcanizates.Weiterlesen...

Single-Stage Profile Coextrusion of Rubber and Thermoplastics into recyclable Sealing Profiles
In a research project, the single-stage coextrusion of EPDM and PE-LD was realised. A novel coextrusion die was designed rheologically and thermally. During the co-extrusion trials, the die temperature and the screw speed were varied. Subsequently, the rubber was vulcanised by microwave and infrared radiation, which could easily be stopped from heating up the thermoplastic. It could be shown that coextrudates of EPDM and PE-LD can be produced in a reasonably stable extrusion process. The adhesive strength of the two layers was so high that it was not possible to carry out peeling tests. The material combination offers the possibility of reusing rejected production runs as a TPE material.Weiterlesen...